- Home
- Knowledge library
- Arable weeds: Basic black-grass biology
Arable weeds: Basic black-grass biology
Integrated control strategies require a good understanding of black-grass weed biology. Find out more about the life cycle of this key arable weed to help you beat it.
How to manage black-grass in arable crops
The encyclopaedia of arable weeds
Where is black-grass found?
Geographic location
Distributed all over the British Isles, black-grass (Alopecurus myosuroides) is most abundant in cultivated land in South-East England. However, it has gradually spread North and West, recently arriving in South-East Scotland and Northumberland. It remains rare in northern Scotland.
Soil type
Black-grass is found on heavy and light soils, but thrives on heavy, poorly drained soils.
What does black-grass look like?
This annual grass weed has upright, round and slender stems with few nodes. The young leaves are fine and smooth with a shiny upper surface. The leaf blade is twisted with a blunt tip. The lower sheath of larger seedlings is often purple. Black-grass grows in graceful tufts. The very narrow, dark purple flowerhead is packed with single-flowered spikelets. It can reach up to up to 85 cm in height.

Lookalikes
Black-grass can be confused with loose silky-bent at the young plant stage of development. This is due to the reddish/purple colouring of the leaf sheath; however, silky-bent tends to prefer lighter soils.
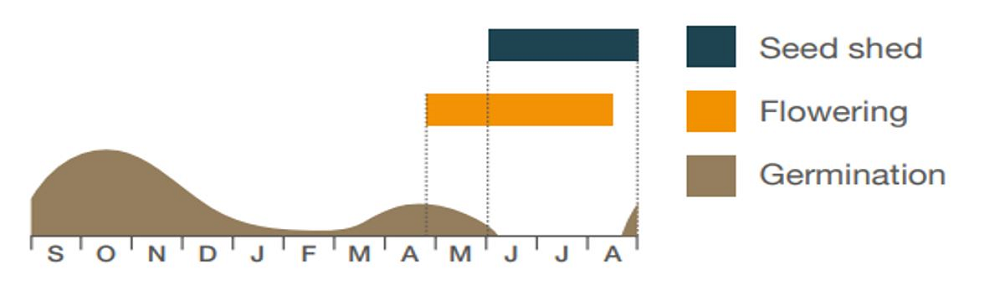
Basic black-grass biology
- Seeds produced in high numbers
- Seeds shed before crop harvest
- Average seed decline in the soil is 75% per year
- Seed dormancy and soil moisture/temperature affect emergence patterns
- Low dormancy occurs in warm, dry conditions
- Seeds often grow rapidly (providing moisture is not limiting)
- Most black-grass emerges from seeds within 5 cm of the soil surface
- Most plants (about 80%) emerge in early autumn
- Black-grass can continue to emerge from clods broken down during winter
- There is very little spring emergence from undisturbed soils
- In some years, black-grass germinates as the crop ripens
- Plants tiller in early spring
Life cycle
 AHDB
AHDB
Black-grass seed statistics
- Seed longevity: 1–5 years
- Seed decline: 80% per year
- Germination depth: 5.7 cm
- Seed weight: 1.8 mg
- Seeds/head: 100
- Seeds/plant: 800
Further information
How to manage black-grass in arable crops
When was this information last updated?
This page is based on content from the encyclopaedia of arable weeds publication. Since it was first released in 2008, the publication has been redesigned several times but not revised. However, it remains a good foundation for general information on the distribution and biology of weeds.

